What to Eat to Reduce Inflammation, Support Gut Health, and Protect Long-Term Wellness
Thank you for reading this post, don’t forget to subscribe!Inflammation is at the root of nearly every modern chronic health condition — from digestive issues and hormonal imbalance to joint pain, fatigue, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders. While inflammation is a natural and necessary part of healing, chronic inflammation is not — and diet plays a powerful role in determining which type dominates your body.
This complete guide to anti-inflammatory foods is designed to help you understand what inflammation really is, how food influences it at a cellular level, and exactly what to eat to calm inflammation naturally. Backed by current research and practical nutrition principles, this pillar article will walk you through 20 of the most effective anti-inflammatory foods, how to build meals around them, and how to turn this knowledge into a sustainable lifestyle.
Whether you’re struggling with bloating, low energy, joint discomfort, or simply want to protect your long-term health, this guide will give you a clear, science-backed roadmap — without restriction, perfection, or overwhelm.
Table of Contents
- What Is Inflammation?
- Acute vs Chronic Inflammation (Why It Matters)
- How Food Influences Inflammation
- Top 20 Anti-Inflammatory Foods (Science-Backed)
- Foods That Promote Inflammation
- How to Build an Anti-Inflammatory Plate
- Anti-Inflammatory Meal Planning
- Simple Anti-Inflammatory Recipes
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Downloadable Anti-Inflammatory Foods Chart
What Is Inflammation?
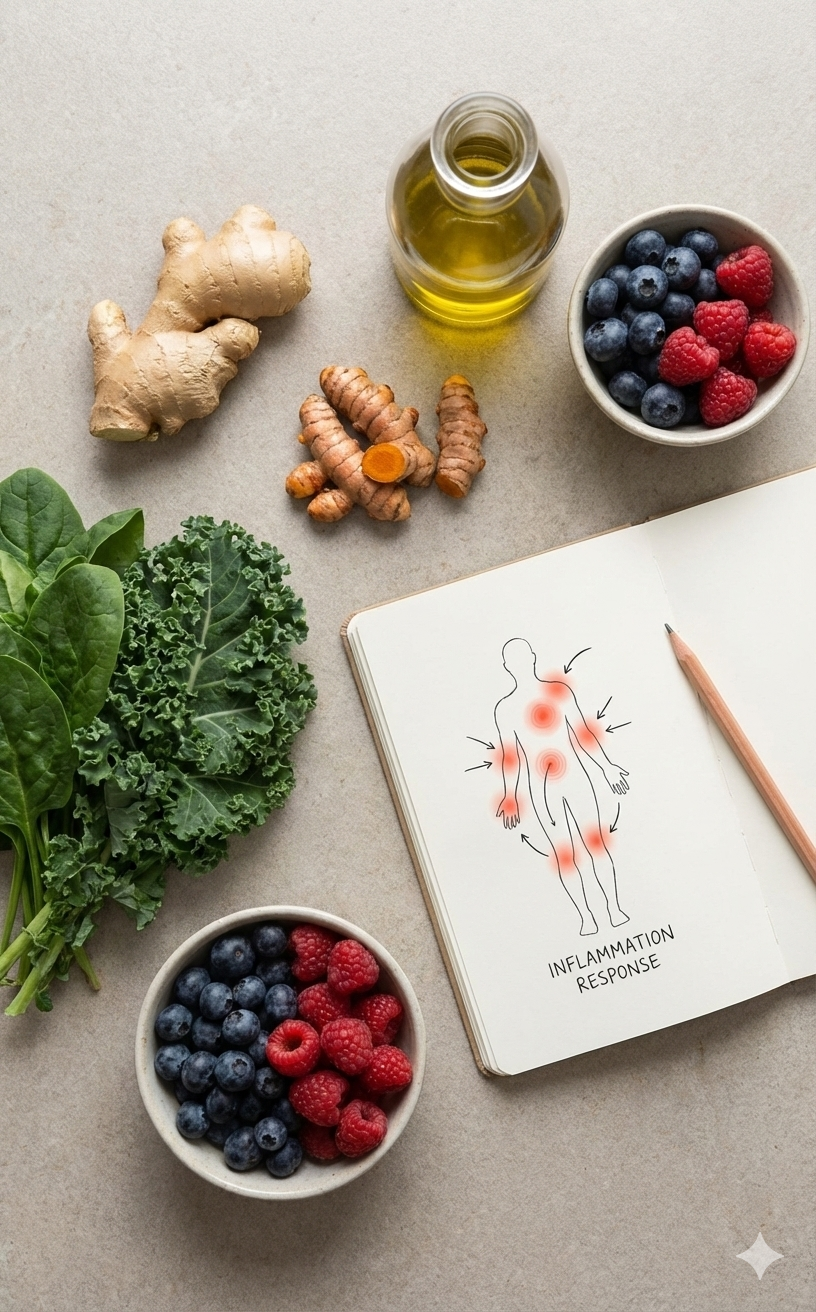

Inflammation is your body’s built-in defense system. It’s how your immune system responds to injury, infection, or perceived threats. When you cut your finger, catch a virus, or recover from exercise, inflammation helps initiate healing.
The problem arises when inflammation doesn’t shut off.
Chronic inflammation is a low-grade, persistent immune response that silently damages tissues over time. Unlike acute inflammation, it often doesn’t come with obvious symptoms — which is why many people don’t realize it’s happening until health issues appear.
Chronic inflammation has been strongly linked to:
- Digestive disorders and gut permeability
- Autoimmune conditions
- Cardiovascular disease
- Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- Hormonal imbalance
- Brain fog and fatigue
Emerging research also shows that dietary patterns, not individual nutrients, play one of the largest roles in either promoting or reducing inflammation.
👉 For a deeper look at how inflammation and digestion are connected, see our guide on gut health and the microbiome.
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation: Why the Difference Matters
| Acute Inflammation | Chronic Inflammation |
|---|---|
| Short-term | Long-term |
| Necessary for healing | Damaging over time |
| Triggered by injury or illness | Driven by diet, stress, lifestyle |
| Resolves naturally | Often silent |
Acute inflammation is helpful. Chronic inflammation is not.
The most common contributors to chronic inflammation include:
- Highly processed foods
- Excess added sugar
- Refined carbohydrates
- Omega-6 heavy vegetable oils
- Chronic stress and poor sleep
- Gut microbiome imbalance
The encouraging news? Dietary changes can reduce inflammatory markers within weeks.
How Food Influences Inflammation

Food communicates with your immune system constantly. Every meal either sends signals that promote balance — or signals that keep inflammation active.
Here’s how food impacts inflammation:
1. Blood Sugar Regulation
Frequent blood sugar spikes trigger inflammatory pathways. Diets high in refined carbs and sugar increase insulin demand and oxidative stress.
2. Gut Microbiome Health
Your gut houses over 70% of your immune system. Fiber-rich, plant-forward diets promote beneficial bacteria that produce anti-inflammatory compounds like short-chain fatty acids.
3. Fat Balance
Modern diets tend to be heavy in omega-6 fats and low in omega-3s. This imbalance promotes inflammation at a cellular level.
4. Antioxidant Intake
Polyphenols and antioxidants neutralize free radicals that contribute to inflammatory damage.
This is why Mediterranean-style and plant-diverse diets consistently rank highest for inflammation reduction in research.
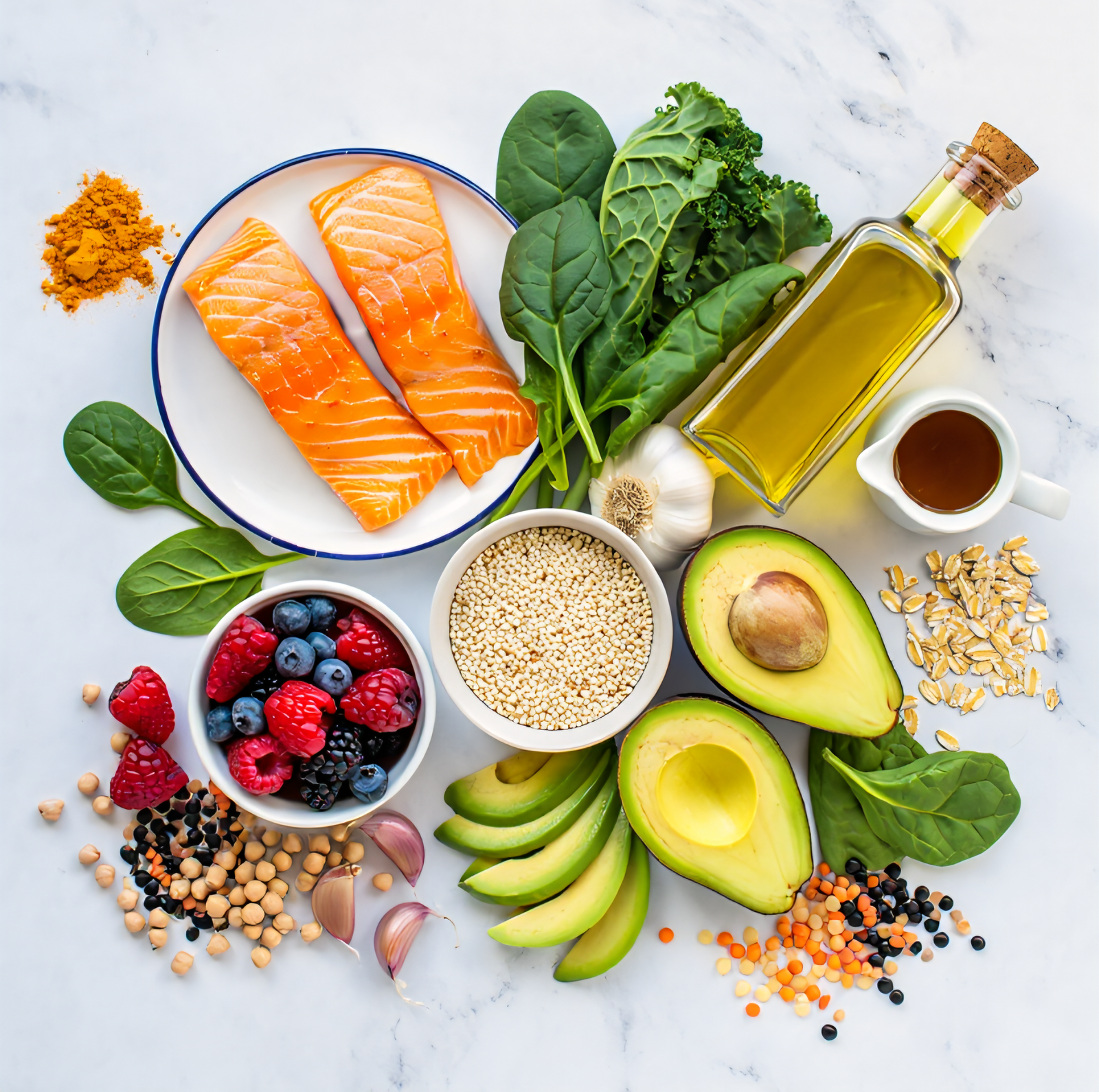
Top 20 Anti-Inflammatory Foods (Science-Backed)
Below are 20 of the most effective anti-inflammatory foods, with practical ways to use them.

1. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Sardines, Mackerel)
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids (EPA & DHA), fatty fish help reduce inflammatory markers like CRP.
How to eat:
Grilled salmon, canned sardines, fish bowls
🔗 Related: One-Pan Salmon & Veggies
2. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Contains oleocanthal — a compound with anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen.
How to eat:
Salad dressings, drizzle over vegetables
3. Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Arugula)
High in antioxidants, fiber, and magnesium.
How to eat:
Smoothies, salads, sautéed greens
4. Berries (Blueberries, Strawberries, Raspberries)
Packed with anthocyanins that reduce oxidative stress.
How to eat:
Oatmeal, yogurt, smoothies
5. Turmeric
Curcumin is a powerful anti-inflammatory compound.
Tip: Pair with black pepper to enhance absorption.
6. Ginger
Reduces inflammatory cytokines and supports digestion.
7. Garlic
Supports immune balance and gut health.
8. Onions
Rich in quercetin, a natural anti-inflammatory flavonoid.
9. Tomatoes
High in lycopene, especially when cooked.
10. Avocados
Contain monounsaturated fats and antioxidants.
11. Nuts (Walnuts, Almonds)
Provide omega-3s and fiber.
12. Seeds (Chia, Flax, Hemp)
Support hormone balance and gut health.
13. Green Tea
Contains EGCG, a powerful antioxidant.
14. Dark Chocolate (70%+)
Rich in polyphenols — moderation matters.
15. Legumes (Lentils, Chickpeas, Beans)
High in fiber and plant protein.
16. Cruciferous Vegetables (Broccoli, Cauliflower)
Support detox pathways and reduce inflammation.
17. Mushrooms
Contain beta-glucans that support immune regulation.
18. Whole Grains (Oats, Quinoa)
Provide fiber that feeds gut bacteria.
19. Fermented Foods (Yogurt, Kefir, Sauerkraut)
Improve gut integrity and immune signaling.
20. Herbs & Spices
Cinnamon, rosemary, oregano, basil all contribute anti-inflammatory compounds.
Foods That Promote Inflammation
While perfection isn’t required, reducing these foods helps calm inflammation:
- Refined sugar
- Ultra-processed snacks
- Refined grains
- Trans fats
- Excess alcohol
Think reduction, not elimination.
How to Build an Anti-Inflammatory Plate
A simple framework:
- ½ plate: vegetables
- ¼ plate: protein
- ¼ plate: whole grains or legumes
- Healthy fats: olive oil, avocado
- Flavor: herbs & spices
This approach naturally balances blood sugar, fiber, and fats.
Anti-Inflammatory Meal Planning

Beginner Tips:
- Focus on adding foods, not restricting
- Batch cook grains and proteins
- Use frozen vegetables for convenience
Advanced Tips:
- Rotate plant foods weekly
- Include fermented foods daily
- Balance omega-3 intake
🔗 Related: 7-Day Gut-Healing Meal Plan
Simple Anti-Inflammatory Recipes
- Anti-inflammatory smoothie bowl
- One-pan salmon & veggies
- Lentil vegetable soup
- No-bake energy balls
- Turmeric golden milk
(Each links to full recipe posts.)
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast can diet reduce inflammation?
Markers can improve in as little as 2–4 weeks.
Is coffee inflammatory?
In moderation, coffee is generally anti-inflammatory.
Is dairy inflammatory?
Depends on the individual. Fermented dairy is often better tolerated.
Downloadable Anti-Inflammatory Foods Chart
👉 Download the Free Anti-Inflammatory Foods Chart (Printable PDF)
Includes:
- Top foods to eat
- Foods to limit
- Nutrient highlights
- Easy reference format

(Perfect fridge or pantry guide.)
Final Thoughts
Reducing inflammation isn’t about perfection — it’s about consistent, nourishing choices that support your body’s natural healing systems.
By prioritizing whole, fiber-rich, antioxidant-packed foods, you create an internal environment that allows your immune system, gut, and hormones to function as they were designed to.
Start with one small change this week — and let your food work for you, not against you.